Vector recreation of the Zeiss logo as around 1975
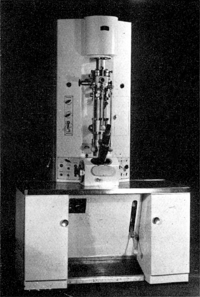
Zeiss is a German Manufactuer of Electron Microscopes, much like Siemens it was involved in the invention of the Electron Microsocpe. Originally its development focused on the creation of Electrostatic microscopes, but this approch was later abbandoned in favor of the Electromagnetic lens.
Only 2 models using exclusivly Electrostic Lenses are currently known to have existed, this is the experimental EM7, and the production EM8 microscope.
The EM9 marked the first all Electromagnetic Electron Microscope constructed by Carl Zeiss.
List of Models Transmition Electron Microscopes Early Models
EM7
General
Year
Successor
EM8
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Cathode Type
Accelerating Voltage
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electrostatic
Stage
Holder Type
X, Y Travel Range
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Å
Lens Type
Electrostatic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Avalible Polpeace Magnification(s)
Alignment
Lens Type
Electrostatic
EM8
General
Year
Successor
EM9
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Cathode Type
Accelerating Voltage
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electrostatic
Stage
Holder Type
X, Y Travel Range
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Å
Lens Type
Electrostatic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
2
Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Avalible Polpeace Magnification(s)
Alignment
Lens Type
Electrostatic
EM9
General
Year
Successor
EM10
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Cathode Type
Accelerating Voltage
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
X, Y Travel Range
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Å
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Avalible Polpeace Magnification(s)
Alignment
Lens Type
General
Year
1947
Successor
EM8
Mag. Range
1500x, 5000x, 15000xM
Electron Source
Acellerating Voltage
60 KV (50 KV)
Objective
Lens Type
Electrostatic
Resolution
20Å
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electrostatic
No. of Lenses
2
General
Successor
EM9
Mag. Range
900x, 1.6Kx, 3Kx, 5Kx, 9Kx, 16Kx
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Steigerwald remote focus Triode
Acellerating Voltage
60 KV
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Objective
Lens Type
Electrostatic
Stigmator
Electrostatic Hexapol
Resolution
7-9Å
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electrostatic
No. of Lenses
3
General
Successor
EM10
Mag. Range
1800x, 8000x, 26Kx, 60Kx, 0-60Kx
Mag. Gauge
Text and Bulb
Power Requirment
1.8 KVA
System Weight
1320 lbs
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Acellerating Voltage
60 KV
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Nu. of Lenses
1
Stage
Holder Type
Side Entry
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Focal Length
4mm
Stigmator
Electrostatic Octopol
Resolution
7-9Å
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
2
Configuration
Single Polpiece
Orange Column Models It should be noted that this list is far from complete, and many models are yet missing within!
General
Successor
EM10A
Mag. Range
100x, 1000x - 200Kx
Mag. Gauge
7-Seg. Digital
Chamber Pressure
5*10⁻⁵ Torr
Power Requirment
3.5 KVA
System Weight
800 Kg
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Acellerating Voltage
20, 40, 60, 80, 100 KV
Stability
2*10⁻⁶min
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Cathode Heating
DC
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Nu. of Lenses
2
Stability
5*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Quadropol
Spot Size
1 µm
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Focal Length
2.6mm
Stability
2*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Octopol
Spherical Error
2.2 mm
Chromatic Error
1.7 mm
Resolution
5Å
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
2
Stability
2*10⁻⁶/min
Configuration
Single Polpiece
Stigmator
Octopol
General
Successor
EM10C
Mag. Range
100x, 1000x - 200Kx
Mag. Gauge
7-Seg. Digital
Chamber Pressure
5*10⁻⁵ Torr
Power Requirment
3.5 KVA
System Weight
800 Kg
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Acellerating Voltage
20, 40, 60, 80, 100 KV
Stability
2*10⁻⁶min
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Cathode Heating
DC
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Nu. of Lenses
2
Stability
5*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Quadropol
Spot Size
1 µm
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Focal Length
2.6mm
Stability
2*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Octopol
Spherical Error
2.2 mm
Chromatic Error
1.7 mm
Resolution
5Å
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
2
Stability
2*10⁻⁶/min
Configuration
Single Polpiece
Stigmator
Octopol
General
Successor
EM10CR
Mag. Range
100x, 1000x - 500Kx
Mag. Gauge
7-Seg. Digital
Chamber Pressure
5*10⁻⁵ Torr
Power Requirment
3.5 KVA
System Weight
800 Kg
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Acellerating Voltage
20, 40, 60, 80, 100 KV
Stability
2*10⁻⁶min
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Cathode Heating
DC
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Nu. of Lenses
2
Stability
5*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Quadropol
Spot Size
200 nm
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Focal Length
2.6mm
Stability
2*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Octopol
Spherical Error
2.2 mm
Chromatic Error
1.7 mm
Resolution
3Å
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
2
Stability
2*10⁻⁶/min
Configuration
Single Polpiece
Stigmator
Octopol
General
Successor
EM10CR
Mag. Range
100x, 1000x - 500Kx
Mag. Gauge
7-Seg. Digital
Chamber Pressure
5*10⁻⁷ Torr
Power Requirment
3.5 KVA
System Weight
800 Kg
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Acellerating Voltage
20, 40, 60, 80, 100 KV
Stability
2*10⁻⁶min
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Cathode Heating
DC
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Nu. of Lenses
2
Stability
5*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Quadropol
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Focal Length
2.6mm
Stability
2*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Octopol
Spherical Error
2.2 mm
Chromatic Error
1.7 mm
Resolution
3Å
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
2
Stability
2*10⁻⁶/min
Configuration
Single Polpiece
Stigmator
Octopol
General
Mag. Range
150x, 1100x, 3000x, 20Kx, 30Kx, 250Kx, 400Kx
Mag. Gauge
7-Seg. Digital
Chamber Pressure
2*10⁻⁶ Torr
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Acellerating Voltage
50, 80 KV
Stability
8*10⁻⁶min
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Cathode Heating
DC
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Nu. of Lenses
2
Stability
6*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Quadropol
Spot Size
3 µm
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Focal Length
2.6mm
Stability
4*10⁻⁶/min
Stigmator
Octopol
Spherical Error
2.2 mm
Chromatic Error
1.7 mm
Resolution
5Å
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
3
Stability
6*10⁻⁶/min
Configuration
Single Polpiece
Stigmator
Octopol
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Documentation Full list of all documents related to the Zeiss Electron Microscopes.
Transmission Electron Microscope English
German
EM8
EM9A
EM10A/B
EM10C/CR
Scanning Electron Microscope Miscilanious stuff
↑ Das Elektronenmikroskop TEM+REM, Dr. Rainer Horst Lang, Dr. Jochen Blödorn, 1981, page 131
↑ Das Elektronenmikroskop TEM+REM, Dr. Rainer Horst Lang, Dr. Jochen Blödorn, 1981, page 132
↑ Das Elektronenmikroskop TEM+REM, Dr. Rainer Horst Lang, Dr. Jochen Blödorn, 1981, page 133