Line 7:
Line 7: ==Transmission Electron Microscops new ==
==Transmission Electron Microscops new ==
test
test
− {{#DeviceInfoBox:tem|Prototyp 1|File:Siemens - Prototyp.png|
+ {{#DeviceInfoBox2 :tem|Prototyp 1|File:Siemens - Prototyp.png|
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
year=1938;
year=1938;
Line 21:
Line 21: |}}
|}}
− {{#DeviceInfoBox:tem|Prototyp 2|File:Ruska Prototype 3 - meek.jpg|
+ {{#DeviceInfoBox2 :tem|Prototyp 2|File:Ruska Prototype 3 - meek.jpg|
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
year=1938;
year=1938;
Line 36:
Line 36: |}}
|}}
− {{#DeviceInfoBox:tem|Übermikroskop|File:Siemens - Übermikroskop - Meek.jpg|
+ {{#DeviceInfoBox2 :tem|Übermikroskop|File:Siemens - Übermikroskop - Meek.jpg|
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
year=1939;
year=1939;
Line 51:
Line 51: |}}
|}}
− {{#DeviceInfoBox:tem|ÜM100|Siemens - ÜM100 - Ruska 1953.png|
+ {{#DeviceInfoBox2 :tem|ÜM100|Siemens - ÜM100 - Ruska 1953.png|
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
year=1949;
year=1949;
Line 66:
Line 66: |}}
|}}
− {{#DeviceInfoBox:tem|Elmiskop I|File:Elmiskop1-Front-Brochure.jpg|
+ {{#DeviceInfoBox2 :tem|Elmiskop I|File:Elmiskop1-Front-Brochure.jpg|
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
OEM=File:Siemens & Halske - Logo - 1971.png;
year=1954;
year=1954;
Revision as of 23:57, 12 February 2022
The Siemens Logo as seen in 1971
The Siemens Corperation has, throughout the years produced many things, among them was the very First Electron Microsocpe . The history of the Electron Microscope started with Siemenes and Ernst Ruska, together with his research team, they created the very first Electron Microscopes.
Models Siemens, as the company responsible for the invention of the Electron Microscope has produced many models throughout the years, also selling a rebadged version of the Etec Autoscan which was sold under the Siemens name outside the United States. Most of their models however where of the Transmission kind, mostly due to Ernst Ruskas Prescience.
Transmission Electron Microscops new test
General
Year
1938
Successor
Prototyp 2
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Kanalstrahlrohr
Acellerating Voltage
75 KV
Cathode
Gas Discharge
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
1
General
Year
1938
Successor
Übermikroskop
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Kanalstrahlrohr
Acellerating Voltage
75 KV
Cathode
Gas Discharge
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Resolution
100a
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
1
General
Year
1939
Successor
ÜM100
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Kanalstrahlrohr
Acellerating Voltage
75 KV
Cathode
Gas Discharge
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Resolution
100a
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
1
General
Year
1949
Successor
Elmiskop I
Chamber Pressure
10e-4 Torr
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Acellerating Voltage
40 KV, 60 KV, 80 KV, 100 KV
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
1
General
Year
1954
Successor
Elmiskop IA
Mag. Range
200x - 200Kx
Mag. Gauge
Galvanometer
Chamber Pressure
10e-4 Torr
Power Requirment
3.3 KVA
System Weight
1200 Kg
Electron Source
Accelerator Type
Self Biased Triode
Acellerating Voltage
40, 60, 80, 100 KV
Stability
2*10⁻⁵/min
Cathode
Tungsten Hairpin
Cathode Heating
AC
Condenser
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Nu. of Lenses
2
Stability
10⁻³/min
Stigmator
Moveing Iron
Spot Size
2µm
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entery
Objective
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Focal Length
2.8mm
Stability
10⁻⁵/min
Range
2.8mm to 7.4mm
Resolution
5Å
Projective Lens
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
No. of Lenses
2
Stability
10⁻⁴/min
Configuration
4 Polpiece Revolver
Pol Piece Mag.
12.5:1, 31.2:1, 62.5:1, 125:1, 250:1
Manual
Service Documentation
Promotional
Research Papers
Transmission Electron Microscops
High Speed Oscillograph Electron Source
General
Year
1933
Successor
Prototype 1
Magnification Range
N/A
Magnification Gauge Type
N/A
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻3 Torr
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Kanalstrahlrohr
Cathode Type
Gas Discharge
Accelerating Voltage
75 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
N/A
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
2
Current Stability
Stigmator
N/A
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
N/A
Objective Lens
Focal Length
N/A
Adjustment Range
N/A
Spherical Error
N/A
Current Stability
N/A
Stigmator
N/A
Alignment Aids
N/A
Point Resolution
N/A
Lens Type
N/A
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
N/A
Current Stability
N/A
Polpeace Configuration
N/A
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
N/A
Alignment
N/A
Lens Type
N/A
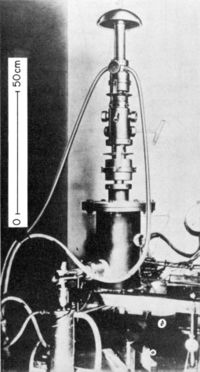
Prototyp 1
General
Year
1933
Successor
Prototype 2
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻3 Torr
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Kanalstrahlrohr
Cathode Type
Gas Discharge
Accelerating Voltage
75 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
N/A
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
1
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
N/A
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
500 Å [1]
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Single Polpiece
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
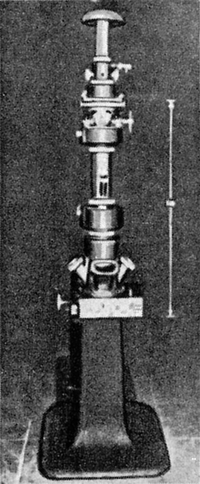
Prototyp 2
General
Year
1938
Successor
Prototype 3
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻3 Torr?
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Kanalstrahlrohr
Cathode Type
Gas Discharge
Accelerating Voltage
75 KV?
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
N/A
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
1
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
N/A
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Single Polpiece
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Prototyp 3
General
Year
1938
Successor
Übermikroskop
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻3 Torr?
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Kanalstrahlrohr
Cathode Type
Gas Discharge
Accelerating Voltage
75 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
N/A
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
1
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
N/A
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
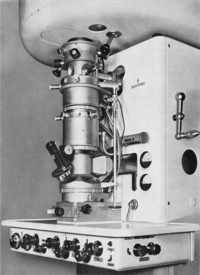
100 Å [2]
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Single Polpiece
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Übermikroskop
General
Year
1939
Successor
ÜM100
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻4 Torr?
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Kanalstrahlrohr
Cathode Type
Gas Discharge
Accelerating Voltage
75 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
N/A
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
1
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
100 Å [3]
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Single Polpiece
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
ÜM100 Gen1
General
Year
1939
Successor
ÜM100
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻4 Torr?
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
55, 70, 85, 100 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
1
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Single Polpiece
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
ÜM100
General
Year
1949
Successor
Elmiskop I
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻4 Torr?
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
40, 60, 80, 100 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
1
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Single Polpiece
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
ÜM60
General
Year
1950
Successor
Elmiskop II
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻4 Torr?
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
40, 50, 60 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
N/A
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
1
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Single Polpiece
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Elmiskop I
General
Year
1954
Successor
Elmiskop IA
Magnification Range
200x to 200,000x
Magnification Gauge Type
Galvanometer
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻⁴ Torr
Power Consumption
3.3 KVA
System Weight
1200 Kg
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
40, 60, 80, 100 KV
Stability
2*10⁻⁵/min
Cathode Heating Methode
AC
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
2
Current Stability
10⁻³/min
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
2000 nm
Condensor Alignment
X, Y, and Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
2.8mm
Adjustment Range
2.8mm to 7.4mm
Spherical Error
3.3mm
Current Stability
10⁻⁵/min
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
5 Å
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
10⁻⁴/min
Polpeace Configuration
4 Position Revolver
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
12.5:1, 31.2:1, 62.5:1, 125:1, 250:1
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Elmiskop II Prototype
General
Year
1954
Successor
Elmiskop II
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Galvanometer
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻⁴ Torr
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
40, 50, 60 KV
Stability
style="text-align:center;"
Cathode Heating Methode
AC
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
0
Current Stability
N/A
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
X, Y, and Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
3 * 10⁻⁵/min
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
25 Å [4]
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
4 Position Revolver
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Elmiskop II
General
Year
1955
Successor
Elmiskop 51
Magnification Range
200x to 200,000x
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻⁴ Torr
Power Consumption
2 KVA
System Weight
700 Kg
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
50 KV
Stability
5.35*10⁻9/min
Cathode Heating Methode
AC
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
0
Current Stability
N/A
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
X, Y, and Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
1.8mm
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
3 * 10⁻⁵/min
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
20 Å
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
10⁻⁴/min
Polpeace Configuration
4 Position Revolver
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
16.9:1, 69.9:1, 146:1, 300:1
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Elmiskop 51 Prototyp
General
Year
1956
Successor
Elmiskop 51
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
50 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
AC
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
0
Current Stability
N/A
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry 9 position
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
N/A
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
50 Å [5]
Lens Type
Permanent Magnet
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
N/A
Polpeace Configuration
4 Position Revolver
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Permanent Magnet
Elmiskop IA
General
Year
1961
Successor
Elmiskop 101
Magnification Range
200x to 200,000x
Magnification Gauge Type
Galvanometer
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10⁻5Torr
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
40, 60, 80, 100 KV
Stability
2*10⁻⁵/min
Cathode Heating Methode
AC
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
2
Current Stability
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
X, Y, and Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
4 Å
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
4 Position Revolver
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
12.5:1, 31.2:1, 62.5:1, 125:1, 250:1?
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Elmiskop 51
General
Year
1956
Successor
Elmiskop 51
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
50 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
AC
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
0
Current Stability
N/A
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry 9 position
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
N/A
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
25-50 Å Film Grain Dependent[6]
Lens Type
Permanent Magnet
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
N/A
Polpeace Configuration
4 Position Revolver
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Permanent Magnet
Elmiskop 101
General
Year
1968
Successor
Elmiskop 102
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
40, 60, 80, 100, 125 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
2
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
3-5 Å [7]
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
2 Position Revolver
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Elmiskop 102
General
Year
1972
Successor
Elmiskop 103
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
40, 60, 80, 100, 125 KV
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
2
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
2 Å (Line) 3 Å (Point) [8]
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
1
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Elmiskop 103
General
Year
Successor
Elmiskop 104
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun ?
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin ß
Accelerating Voltage
40, 60, 80, 100, 125 KV ?
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
2
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
1
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Elmiskop 104
General
Year
Successor
none
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun ?
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin ß
Accelerating Voltage
40, 60, 80, 100, 125 KV ?
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
2
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
1
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
X, Y (via Rovolver Rotation) & Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Elmiskop CT150
General
Year
1977
Successor
none
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Cathode Type
Accelerating Voltage
Stability
Cathode Heating Methode
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
Current Stability
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Stage
Holder Type
X, Y Travel Range
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
Scanning Transmission Electron Microscops
Elmiskop ST100F
General
Year
1977
Successor
none
Magnification Range
50x - 10e7X
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
10e-7 mBar
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Crewe FE Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Cold Field Emmision
Accelerating Voltage
20, 40, 60, 80, 100 KV, (10 - 30 KV)
Stability
2*10e-6
Cathode Heating Methode
N/A
Alignment Methode
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
1
Current Stability
2*10e-6
Stigmator
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
Lens Type
Crewe Electrostatic
Stage
Holder Type
X, Y Travel Range
+- 1 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
1.8 mm
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
1.3 mm
Chromatic Error
1.3 mm
Current Stability
1 * 10e-6
Stigmator
Electromagnetic
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
2 Å
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
X-Ray Micro Analyzers
Elmisonde
General
Year
1961
Successor
none
Magnification Range
Magnification Gauge Type
Specemin Chamber Pressure
Power Consumption
System Weight
Electrion Source
Accelerator Type
Single Stage Electron Gun
Cathode Type
Tungsten Hairpin
Accelerating Voltage
40, 60, 80, 100 KV
Stability
2*10⁻⁵/min
Cathode Heating Methode
AC
Alignment Methode
X, Y, Mechanical
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
2
Current Stability
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
X, Y, and Tilt, Mechanical
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
Cartridge, Top Entry
X, Y Travel Range
± 0.8 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Moveing Iron, Mechanical
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Projective Lens
Number of Projective Lens
1
Current Stability
Polpeace Configuration
4 Position Revolver
Avalible Polpeace Magnifications
Alignment
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
Scanning Electron Microscops
Autoscan
General
Year
1972
Successor
none
Magnification Range
20 - 550Kx
Magnification Gauge Type
Analog, (Digital)
Specemin Chamber Pressure
2 * 10-4 Torr
Power Consumption
3 KVA
System Weight
Condensor
Number of Condensor Lenses
3
Current Stability
Stigmator
none
Minimum Spot Size Diameter
Condensor Alignment
none, prealigned
Lens Type
3 gap Common Coil Electromagnetic
Stage
Holder Type
X, Y Travel Range
+- 12.5 mm
Z Travel Range
25 mm
Objective Lens
Focal Length
Adjustment Range
Spherical Error
Current Stability
Stigmator
Dual Quadropol Electromagnetic
Alignment Aids
Point Resolution
7 nm
Lens Type
Electromagnetic
References
↑ Geoffrey A. Meek, Practical Electron Microscopy for the Biologist, 2nd Edition (1976), Page 57
↑ Geoffrey A. Meek, Practical Electron Microscopy for the Biologist, 2nd Edition (1976), Page 58
↑ Geoffrey A. Meek, Practical Electron Microscopy for the Biologist, 2nd Edition (1976), Page 58
↑ K. Müller & E. Ruska, Ein vereinfachtest Elektromagnetisches Durschstahlungsmikroskop für Elektronen von 40 bis 60KV*), 1954
↑ K. Müller & E. Ruska, Ein Hilfselektronenmikroskop für Kurs- und Routinebetrieb, (1956), Vierter Internationaler Kongress für Elektronenmikroskopie, Physikalisch Technischer teil, Page 184-187
↑ Geoffrey A. Meek, Practical Electron Microscopy for the Biologist, 2nd Edition (1976), Page 489
↑ Geoffrey A. Meek, Practical Electron Microscopy for the Biologist, 1st Edition (1970), Page 235
↑ Geoffrey A. Meek, Practical Electron Microscopy for the Biologist, 2nd Edition (1976), Page 502
Documentation Full list of all documents related to the Siemens Electron Microscopes.
Elmiskop I & IA
Price Lists / Catalogs
Categorie Entries Articles in Related to Siemens