Difference between revisions of "Ernst Ruska"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (corrected names) Tags: Mobile web edit Mobile edit |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
{{Tem list entry | {{Tem list entry | ||
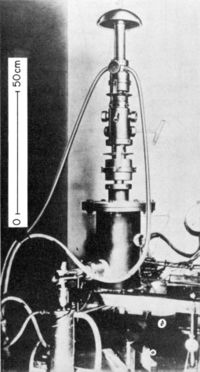
| − | |Microscope Name= | + | |Microscope Name= Prototype 2 |
|Microscope Picture File=Ruska Prototype 1 - meek.jpg | |Microscope Picture File=Ruska Prototype 1 - meek.jpg | ||
|Year=1933 | |Year=1933 | ||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
|Proj. Lens Type=Electromagnetic | |Proj. Lens Type=Electromagnetic | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
== Siemens == | == Siemens == | ||
Latest revision as of 18:17, 17 January 2025
Ernst Ruska was, for all intents and purposes the inventor of the Electron Microscope. He designed and built many such machines over his long life, starting in the university Berlin, and later working for Siemens where he created the famous Elmiskop Series.
He invented the Transmission electron microscope together with his friend Bodo von Borries and Max Knoll.
papers
Transmission Electron Microscopes
University Berlin
These where the devices and Microscopes created by Ernst Ruska during his time at the University of Berlin.
| Prototype 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prototyp 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Siemens
- ↑ Geoffrey A. Meek, Practical Electron Microscopy for the Biologist, 2nd Edition (1976), Page 57